.webp)
- 19 Sep
- 2025
Shaping the Future Through Technical Education | GIST Haldia
Education is the foundation of human progress, but as the world grows increasingly dependent on engineering, and technology, the focus has shifted toward technical education. Unlike general education that emphasizes theoretical knowledge, technical education equips learners with practical skills, applied knowledge, and hands-on training that directly meet industry demands.
Today, technical education is not just a stream of learning—it is the engine that powers economies, drives innovation, and creates skilled professionals ready to face global challenges. From developing future engineers and technicians to preparing students for entrepreneurship and research, technical education forms the backbone of a nation’s development.
In this blog, we’ll explore the multifaceted role of technical education, its impact on careers, industries, and society, and how institutions like Global Institute of Science & Technology (GIST Haldia) are contributing to this mission.
The Concept of Technical Education
Technical education refers to a structured form of learning that focuses on teaching technical skills and vocational knowledge. Unlike traditional academic education that prioritizes theory, technical education ensures learners are trained to design, operate, maintain, and improve technology-driven systems. Its scope is vast, encompassing polytechnic and diploma programs in fields such as mechanical, civil, electrical, and computer engineering, vocational training courses designed for immediate industry applications such as welding or computer networking, and higher technical studies in applied sciences and advanced engineering disciplines. This specialized approach ensures that learners are not only job-ready from the beginning of their careers but also capable of adapting to rapid technological changes.
Historical Evolution of Technical Education
Technical education has existed in some form for centuries. In the ancient era, craftsmanship, metallurgy, and architecture were passed down through apprenticeships and guilds. With the Industrial Revolution in the 18th and 19th centuries, the demand for skilled workers to operate machinery gave rise to vocational schools and technical institutes. The 20th century brought about rapid industrialization, leading to the expansion of technical education and the establishment of polytechnic colleges across the world.
In the 21st century, the digital revolution has placed technical education at the center of economic growth and technological progress. Fields like information technology, artificial intelligence, robotics, renewable energy, and biotechnology now dominate the demand for skilled professionals. This historical journey reflects how technical education has always evolved to align with industrial and societal needs, ensuring progress and modernization.
Importance of Technical Education in the Modern World
In today’s world, technical education holds a place of undeniable importance. It plays a key role in skill development by offering hands-on training in areas such as machine handling, software programming, and construction techniques. This ensures that graduates are not only qualified but also capable of immediately contributing to industry operations. Technical education also enhances employability since courses are directly aligned with market demands, helping students secure stable and rewarding jobs.
Moreover, it fosters innovation and research by equipping students with the knowledge and tools to create practical solutions, whether in the form of sustainable technologies, smart devices, or software applications. On a broader scale, technical education contributes to national development. Countries with strong technical education systems enjoy faster industrial growth, higher productivity, and greater competitiveness on the global stage. Beyond industry and economy, technical education empowers society by providing rural and underprivileged students with opportunities to acquire practical knowledge, enabling them to secure sustainable livelihoods.
Technical Education vs. General Education
General education and technical education serve different but complementary purposes. General education focuses on theoretical knowledge, cultural understanding, and broad intellectual growth, covering areas such as history, literature, and philosophy. Technical education, on the other hand, emphasizes application-driven learning, preparing students for specific industries through courses in mechanical engineering, information technology, or electronics.
While general education nurtures critical thinking and cultural awareness, technical education bridges the gap between theory and practice. Both streams of education are essential, but in today’s global economy, technical education provides the practical edge that ensures employability and career success.
The Role of Technical Education in Career Development
For students, technical education is the stepping stone to a successful career. It provides specialized skills that are in direct demand, such as mastery of industrial machinery, coding, or design software. By offering internships, workshops, and practical sessions, technical education exposes learners to real-world challenges, helping them apply classroom knowledge in professional environments.
Students also develop adaptability through technical training, which allows them to stay relevant in industries that are constantly being reshaped by new technologies such as artificial intelligence, the Internet of Things, and renewable energy. Furthermore, technical education provides an entrepreneurial edge. Many students trained in technical fields go on to create startups, contributing not only to their own success but also to economic development. Thus, technical education nurtures professionals who are not only employable but also capable of leadership and innovation.
Technical Education and Industry Readiness
Industries today are increasingly looking for employees who can contribute effectively from their very first day at work. Technical education prepares students for this demand by creating a strong bridge between classroom learning and industrial application. Institutions often collaborate with companies to provide training and placements, giving students an opportunity to experience industry requirements firsthand.
Through advanced laboratories and workshops, technical education simulates real-world environments, allowing students to practice what they will encounter in their careers. Along with technical skills, many institutions emphasize soft skills training, preparing students in areas such as communication, teamwork, and leadership. This holistic preparation ensures that graduates not only meet industry expectations but are also able to integrate seamlessly into organizational structures.
Challenges in Technical Education
Despite its critical importance, technical education faces several challenges. One major issue is the outdated curriculum, which often lags behind the rapid pace of technological change. While industries evolve quickly, many institutions struggle to update their syllabi to match current needs. Additionally, infrastructure gaps remain a problem, as some colleges lack modern laboratories, equipment, or digital resources necessary for effective training.
Another challenge is the disconnect between academia and industry. Limited collaboration sometimes prevents students from gaining exposure to real-world problems. Accessibility is also a concern, particularly for students from rural or economically weaker backgrounds who may not have access to quality technical education. Lastly, in a globalized job market, students must compete with peers worldwide, making the demand for excellence even higher. Overcoming these challenges requires sustained investment, policy reform, and collaboration between government, academia, and industry.
The Future of Technical Education
The future of technical education is closely tied to technological advancements. In the coming years, subjects like artificial intelligence, robotics, cybersecurity, and data science will become integral parts of technical training. Similarly, as the world focuses on sustainability, there will be a growing need for expertise in renewable energy and green technologies.
Industry 4.0, which focuses on smart manufacturing and automation, will require students to master digital tools and advanced systems. Virtual and augmented reality are also expected to play an important role in teaching by creating immersive learning experiences. As industries become more interdisciplinary, technical education will increasingly blend elements of science, management, and technology, ensuring students are prepared for dynamic careers in evolving sectors.
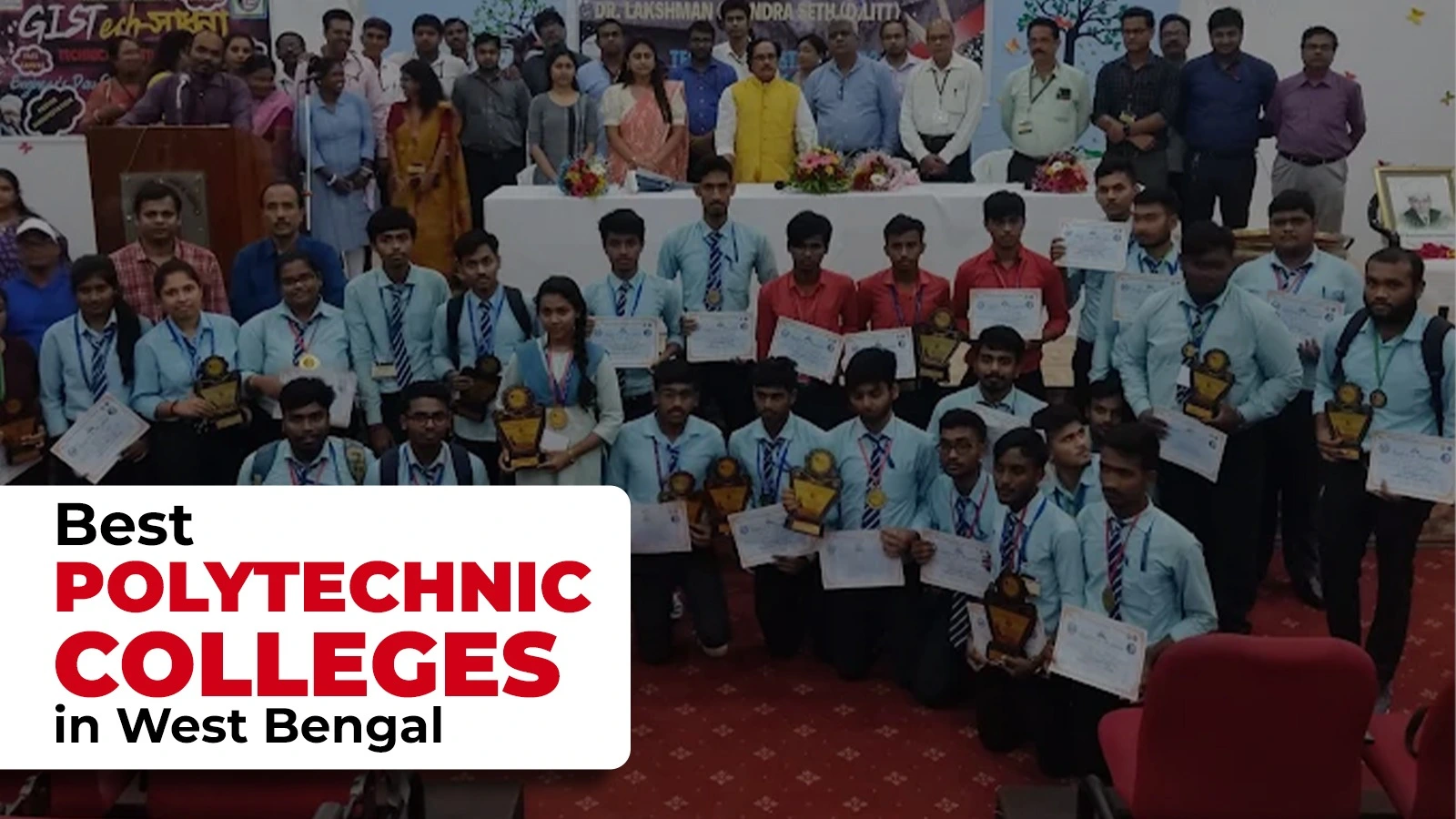
GIST Haldia: A Model of Technical Education Excellence
The Global Institute of Science & Technology (GIST), Haldia, stands as a leading example of how technical education can shape the future. The institution offers diverse diploma programs in mechanical, electrical, civil, and computer science engineering, providing students with practical skills and strong theoretical foundations. With well-equipped laboratories, GIST bridges the gap between theory and practice, allowing students to gain hands-on experience.
The institute actively collaborates with industries, giving students opportunities for real-world exposure through training and internships. Beyond academics, GIST fosters holistic development through NSS, IIC, and cultural activities that nurture leadership, teamwork, and social responsibility. Strong placement support further ensures that graduates transition smoothly into employment or entrepreneurship. In this way, GIST Haldia continues to play a vital role in empowering students and strengthening the technical education ecosystem of West Bengal.
Conclusion
Technical education is much more than creating skilled technicians and engineers. It is about building a workforce capable of innovation, adaptability, and leadership in a rapidly changing world. As industries evolve and societies grow increasingly reliant on technology, the role of technical education will only expand. Institutions like GIST Haldia demonstrate how knowledge and practice can be combined to empower students and contribute to national development.
The journey of shaping the future begins with education, and among the different forms of learning, technical education remains the most powerful tool for transformation. By fostering skills, innovation, and opportunities, technical education ensures that both individuals and societies move confidently toward a brighter and more sustainable future.
Contact Us
Ready to start your journey in technology? Global Institute of Science & Technology, Haldia and take your first step toward a successful tech career.
Address: ICARE Complex, Hatiberia, Haldia – 721657, Purba Medinipur, West Bengal
Phone: +91 3224 252566 / +91 3224 252800
Email: info@gisthaldia.org
Website: www.gisthaldia.org




.webp)
.webp)

.webp)
.webp)








.webp)





.webp)



.webp)

.webp)







.webp)
























.jpg)


.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)



.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)



.jpg)



.jpg)



.jpg)
.jpg)











.png)





.png)







.png)

.png)



